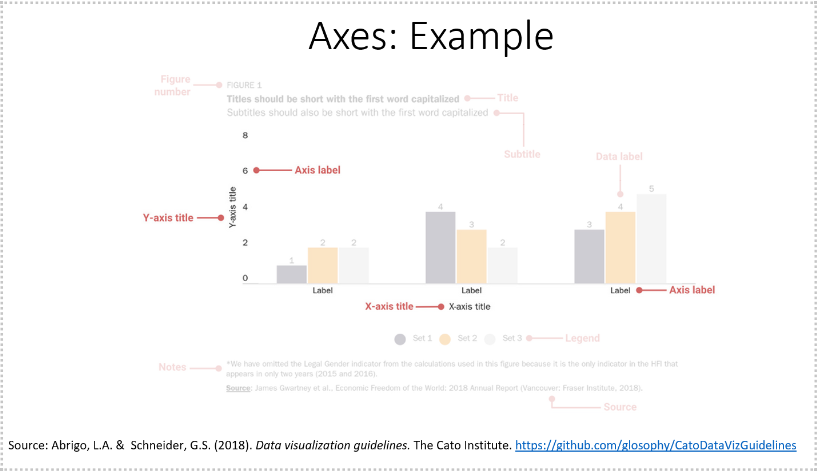
| Compare Values |
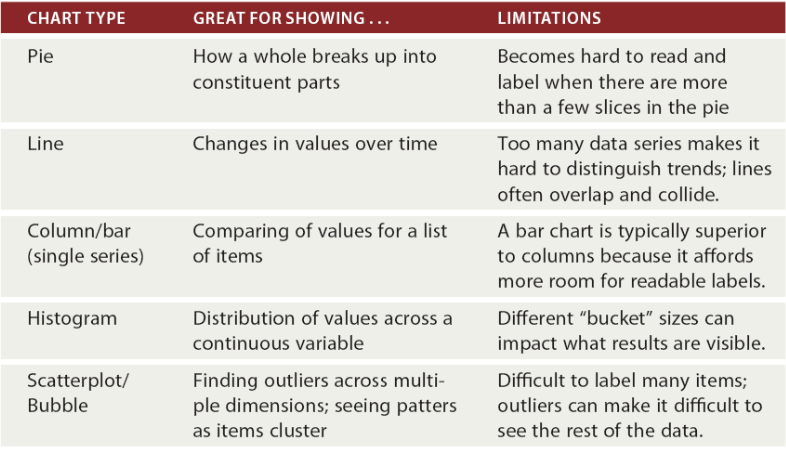
To create a comparison chart, use these types of graphs: Column, Mekko, Bar, Pie (with caution), Line,Scatter Plot, Bullet. |
| Show Composition |
Use this type of chart to show how individual parts make up the whole of something: Pie (with caution), Stacked bar, Mekko, Stacked column, Area, Waterfall |
| Show Distribution |
Distribution charts help you to understand outliers, the normal tendency, and the range of information in your values. Use these charts to show distribution: Scatter plot, Mekko, Line, Column, Bar. |
| Analyze Trends |
- If you want to know more information about how a data set performed during a specific time period, there are specific chart types that do extremely well: Line, Dual-Axis line, column.
- When trying to establish the relationship between things, use these charts: Scatter plot, Bubble, Line Chart.
|
| Understand Relationships between values |
Relationship charts are suited to showing how one variable relates to one or numerous different variables. You could use this to show how something positively effects, has no effect, or negatively effects
another variable. |